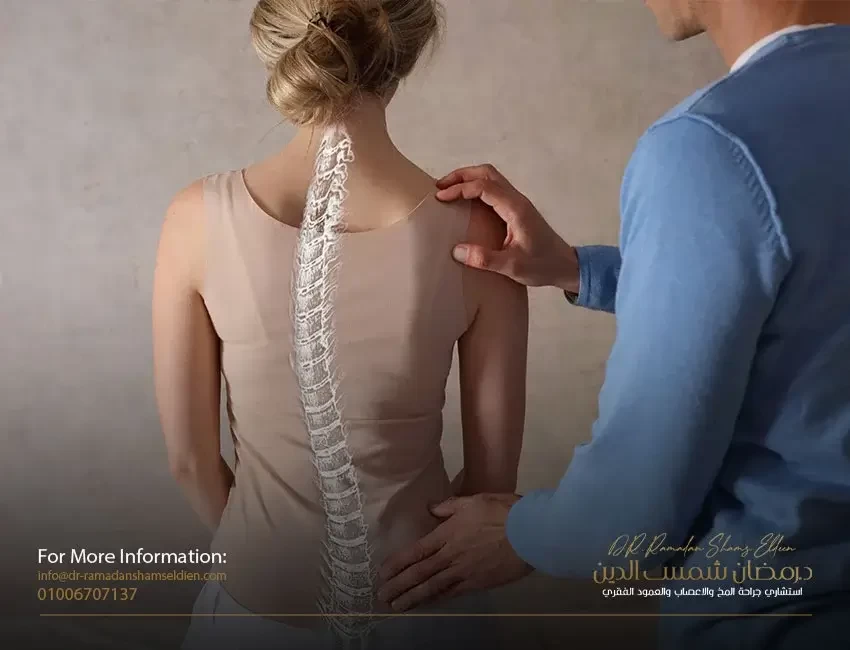
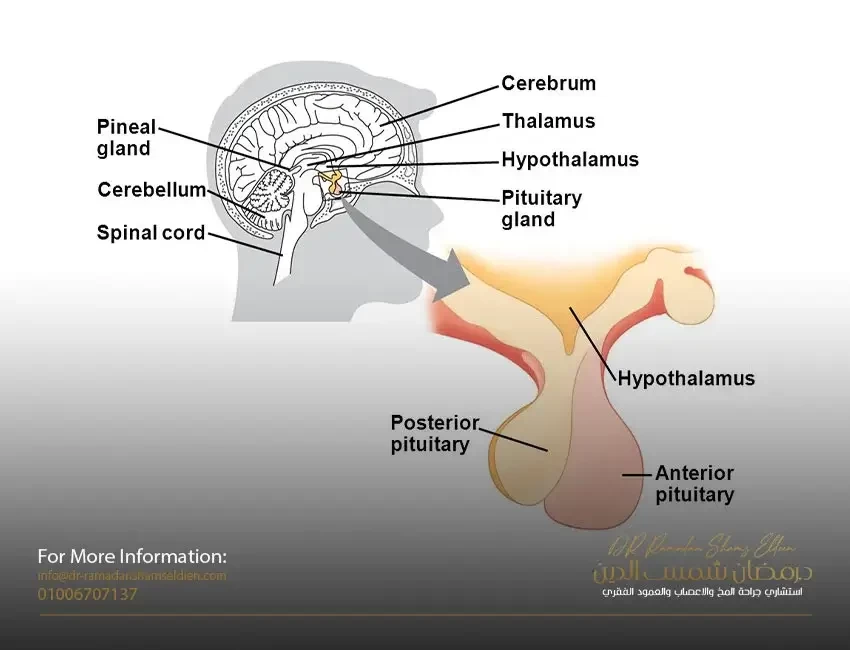
Cauda equina syndrome
It is a rare condition with a disproportionately high legal profile. It frequently occurs after a herniated (bursting) or a large prolapse of the lumbar disc (cartilage) in the middle or center area where the disc or cartilage is against the entire lumbosacral nerve bundle. A review of research indicates that about 70-50% of patients suffer from urinary retention and that 50-30% have incomplete symptoms when presented to a specialist. And this last group would benefit greatly if it was scanned by magnetic resonance imaging and a surgical procedure was performed by an experienced surgeon, as this would avoid the full complications of this dangerous syndrome.
identification
Sye syndrome is usually characterized by the so-called 'red flag' symptoms:
(LBP) • Severe lower back pain
• Sciatica: often bilateral in the lower extremities or one of them more than the other and it is possible the absence of this symptom in some cases
• Total fall or partial weakness of the feet
Urinary retention, bladder and bowel wall weakness, and sexual weakness.
It is critical, both from a medical and a legal medical perspective, that all or all of these “red flag” symptoms are identified and documented.
In particular.
background
Also, when a moderate or even simple lumbar disc herniation occurs in the presence of congenital stenosis of the lumbar neural tube, saddle horse syndrome occurs. Other than cases of lumbar disc herniation, or what is known as lumbar disc herniation, there are less common causes of this syndrome. These causes include: a dura mater tumors, infections, primary and metastatic (or secondary) tumors, trauma after surgery, after spinal anesthesia, epidural hematoma, and finally injuries that lead to direct pressure on the nerve bundle in this area, such as gunshot wounds or fractures. .
It is believed that the incidence rate in the population ranges from 1 in 33,000 to 1 in 100,000 in some European countries and is usually the result of a sudden lumbar disc herniation, except for some rare causes that we mentioned before.
The medical and legal dispute in Cauda equina syndrome occurs because of the disagreement in the understanding and outcome of some issues related to this disease. These controversial issues are:
1. The importance of delays in diagnosis and referral to hospital.
2. Risks and benefits of emergency surgery versus urgent surgery.
3. The importance of surgical delay after 24 and 48 hours.
4. The predictive significance of the involvement of the complete bladder sphincter versus the incomplete and thus the occurrence of urinary retention and complete sensory deficit versus incomplete sensory deficit.
5. Significance of signs of foot drop and unilateral and bilateral leg weakness.
6. Adverse effects of delay on the more powerful roots of the sciatic nerve.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The patient suddenly complains of a set of symptoms and shows some signs that must be quickly explained when the patient is presented to the primary medical service providers, due to the necessity of referring him to specialists. These symptoms and signs are; Severe lower back pain,,, right and left bilateral sciatica pain when the complete syndrome appears or one of them in the incomplete,,,, a complete fall of the feet in the case of the full syndrome syndrome or one of them in the case of the incomplete syndrome,,,,,, Resulting urinary retention About bladder sphincter weakness The diagnosis is made urgently by performing an MRI scan on the lumbar and sacral vertebrae to find out the cause, which, as we mentioned before, is often a sudden rupture or herniation of the lumbar disc in the central region against the fourth, fifth or fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae.
treatment
Urgent surgical intervention at the time the diagnosis is achieved by the specialist before 48 hours have passed from the occurrence of symptoms is the only way to cure this syndrome. This is done through a good expansion of the nerve canal and nerve roots at the site of injury with a discectomy or herniated cartilage. The sooner the intervention, the better the result and the faster the recovery. Also, the intervention in the syndrome of incomplete symptoms, the result of recovery is better than the completed one.