Lumbar herniated disc and lower back pain
Low back pain is one of the most common disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system and is considered the most prevalent in the modern era. It still poses a real health challenge in terms of prevention and treatment, and it ranks third in terms of the high cost of treatment after cardiovascular diseases and cancerous diseases.
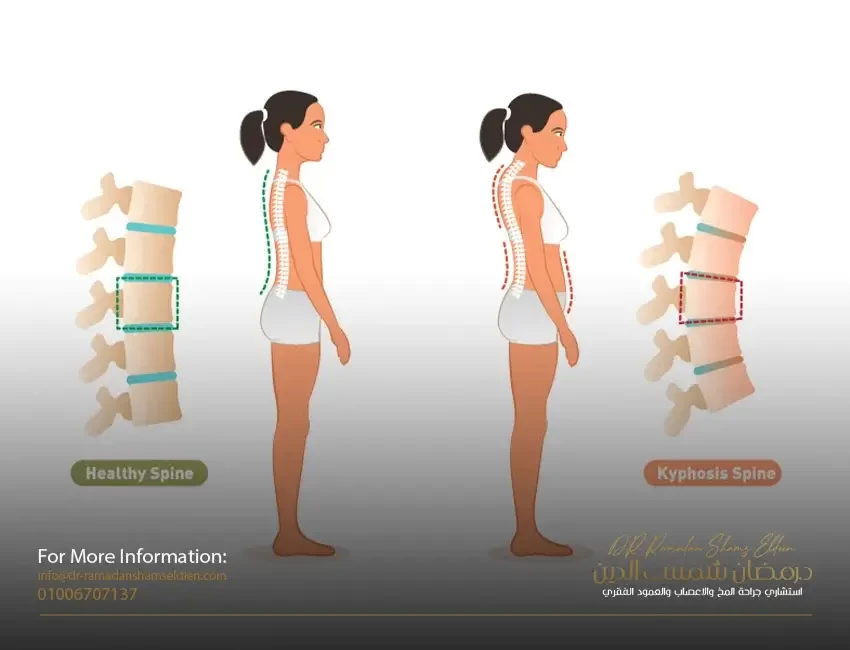
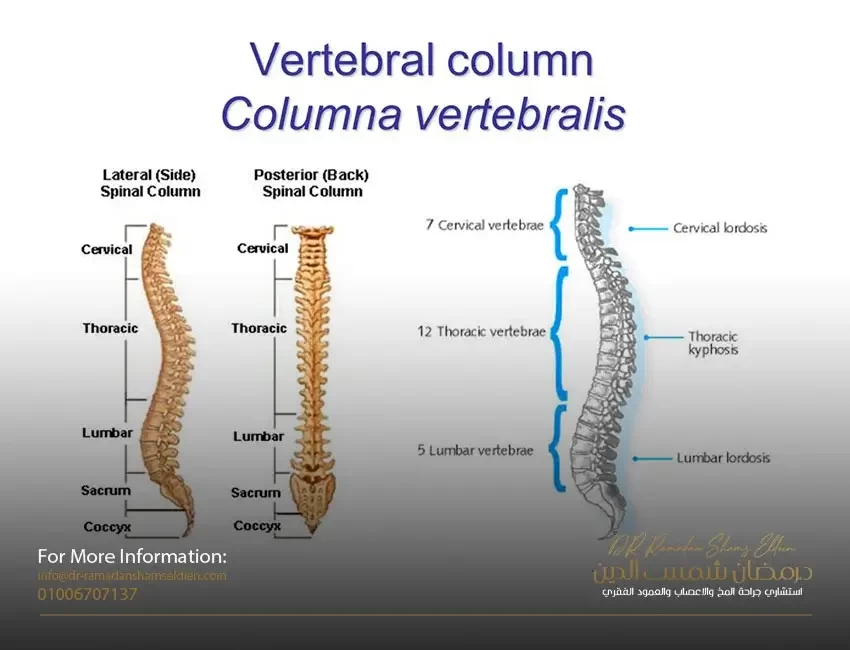
The spine is the only longitudinal axis of the body that bears the entire weight of the trunk, and its lumbar vertebrae are connected with the pelvis and its movement with the sacral vertebrae, and accordingly, any imbalance that affects the body axis (functionally or anatomically) will negatively affect the functional level of the trunk and the movement of the body in general and thus It may reduce psychological, economic and social efficiency, especially when pain appears, which greatly affects the daily activities of the individual and the quality of life he lives. In dispersing the forces acting on it by distributing pressure on the nucleus of the cartilaginous disc, which distributes it equally on the surrounding cartilage rings in all directions over the entire area of the cartilaginous disc. The vertebral congruence condition becomes lost.
Low back pain is usually divided in terms of recurrence into acute, which occurs suddenly and often occurs once or twice in life, and chronic, which occurs frequently, cumulatively and with a higher level of severity with each time.
It is divided in terms of the type of cause into specific mechanical pain, which is directly related to the pain that results from acute muscle strain and herniated disc, which is responsible for 90% of these cases, and to non-mechanical, non-specific pain, which is indirectly related to the pain that results from anxiety states, enlargement of the prostate gland, and dryness. Herniated disc. In terms of the degree of pain, it is divided into simple, medium and severe pain.
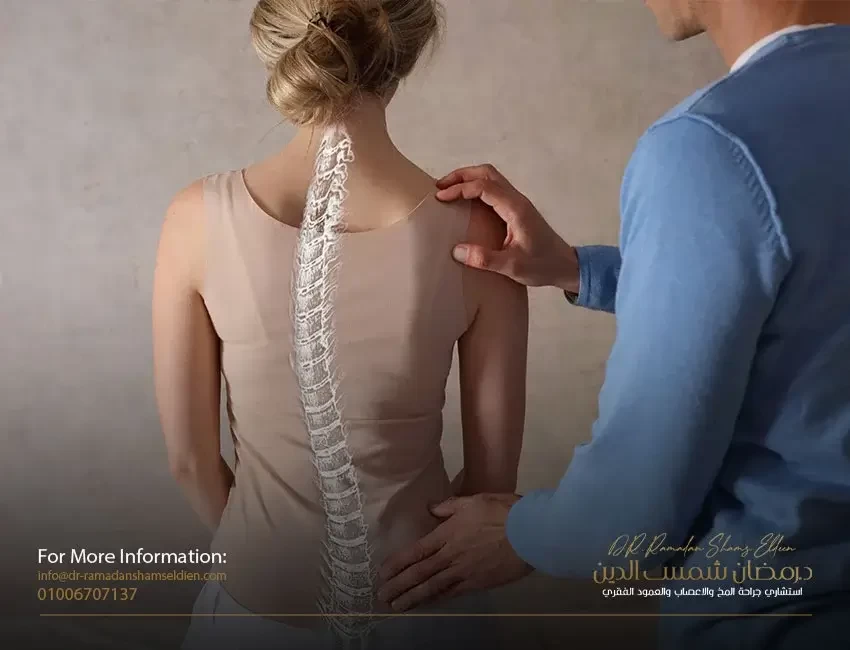
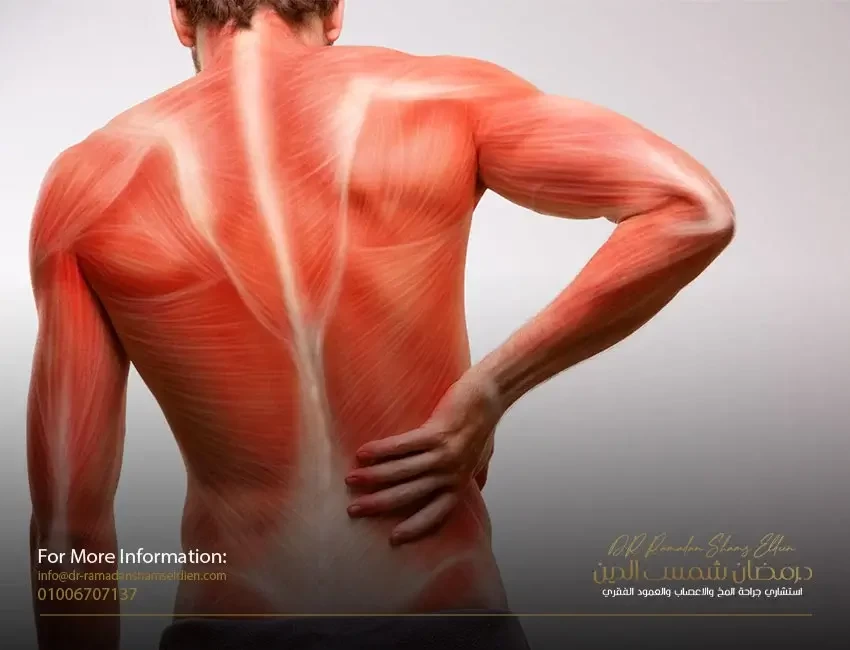
A herniated disc (herniated disc or lumbar disc herniation) is defined as the nucleus and its rings being pushed irregularly from between the vertebrae to the back under the influence of severe pressure with the occurrence of a hernia in the cover of the cartilaginous rings, to grow towards the back to enter the spinal canal and put pressure on the spinal cord. This is called this The condition of the central compressive cartilage. Either it grows backward and to one side and presses on one of the nerve roots branching from the spinal cord. This condition is called the noncentral or lateral compressive cartilage. Regardless of the type of herniated disc or herniated disc in the lumbar disc, it causes severe defensive muscle contractions.
The range of motion between the vertebrae is reduced, in addition to the occurrence of severe pain, and the level of danger is high, as in road accidents, for example, where the pressure is very strong to cause a cartilage rupture with sharp ends that threaten to tear and injure the surrounding tissues and nerves during movement, causing partial or total paralysis of the nerve depending on the force of pressure The severity of the injury to the nerve root.
The most frequent cases are in the lumbar region between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae and between the fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae.
Often, these patients complain of a group of severe neurological disorders represented by sensory impairment and disturbance in
The level of the reflex reaction, weakness in the muscular ability of the lower extremities or one of them, and severe pain in the direction responsible for the nerve root compressed in the herniated disc, which makes this disease a major cause to change the nature of the patient’s psychological, social, economic and family life, especially when it causes any degree of partial or partial disability. total
As for recurrent chronic cases, it is accompanied by a group of functional and anatomical changes on the lower back before the injury of a herniated disc, such as the occurrence of simple long-term muscle tension for many reasons. The cartilage disc reduces the concentration of water in that part of the cartilage, as water - despite its low concentration in the cartilage - plays an essential role in the process of distributing and spreading nutrients within the tissue of the lumbar disc and the speed of completion of vital reactions. With the persistence of muscle tension and the passage of time, this condition is called degenerative lumbar disc dehydration
Then begins a process of functional changes at the level, slowing down the speed of biochemical reactions, as well as anatomical changes in the formation of the lumbar disc, such as a lack of cartilage tissue cohesion and weakness in its elasticity and a decrease in the size and mass of the lumbar disc, so it becomes less able to absorb the forces acting on it, and the process of fibrosis of the spinal canal begins. The nerve roots exits increasingly over time to cause what is known as neural tube stenosis.
This results in sharp pains in the lower back extending to the lower extremities or one of them, with lethargy and weakness and a decrease in the ability to walk because of this, and the ability to straighten the trunk is weakened due to the contact of the cartilaginous protrusion with the nerve roots emerging from the spinal cord.
Most cases of herniated discs of the lumbar disc usually occur between the ages of twenty and forty, with most injuries occurring.
Due to improper lifting of heavy weights or injuries resulting from practicing some sports such as weightlifting and gymnastics, or for former athletes in some sports.
Herniated disc pain is treated medically
With it on the basis of removing the pressure from the cartilage of the cartilage
On the nerves by using the abduction tension
(slitting the vertebrae apart) naturally using positions
body (positional therapy) called stretching