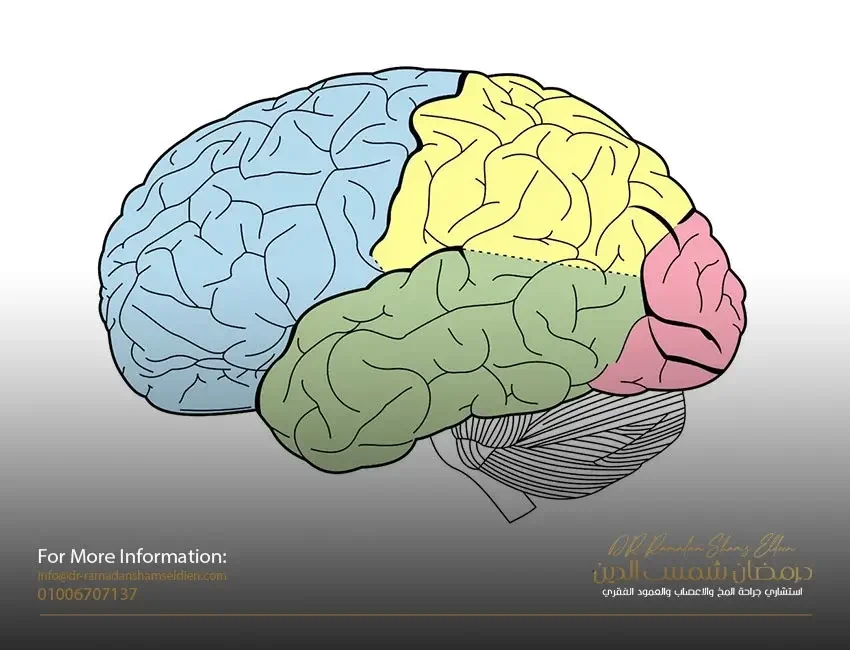
The cerebral cortex is made up of tightly packed neurons, the wrinkled layer, of coils of neurons that surround the brain from the outside. It is also responsible for higher thinking processes including speech and decision making. The cortex is divided into four different lobes, the frontal or frontal, parietal or lateral, temporal or temporal, and occipital or posterior, and each of these four lobes is responsible for processing different functions or types of sensory information.
You can use the frontal or frontal lobe almost every day.
You can use it to make decisions, such as to eat or drink, as well as to think and study.
The frontal lobe is also where our personality is formed and where we can perform higher mental processes such as planning.
In addition, the frontal lobe is necessary for a person to be able to speak fluently (without error) and with meaningful words.
The parietal lobe performs some very specific functions. As part of the cortex, it has a lot of responsibilities and must be able to process sensory information within seconds.
The parietal lobe is where information such as taste, temperature and touch is incorporated or processed. If the parietal lobe was damaged, humans would not be able to feel sensations such as touch, temperature, and taste.
The temporal or temporal lobes mainly function around hearing and selective listening.
It receives sensory information such as sounds and speech from the ears.
It is also the key to being able to comprehend, or understand purposeful speech.
In fact, we would not be able to understand a person speaking to us, if the temporal lobe did not exist.
The occipital or posterior lobe is important to be able to properly understand what the eye sees. It has to work super fast to process the fast information that our eyes send.
Similar to the temporal lobe in auditory information, the occipital lobe is in visual information so that we can understand it. If we have a weakness in the occipital lobe or an injury we will not be able to process the visual signals properly, and thus visual confusion may result.
The cerebellum is one of the most recognizable parts of the brain due to its unique shape and location.
It is extremely important to be able to perform daily voluntary tasks (doing with purpose and intent) such as walking and writing.
It is also essential to be able to stay balanced and straight.
Patients who have suffered from cerebellar damage often struggle to maintain their balance and maintain proper muscle coordination and often cannot do this normally and completely.
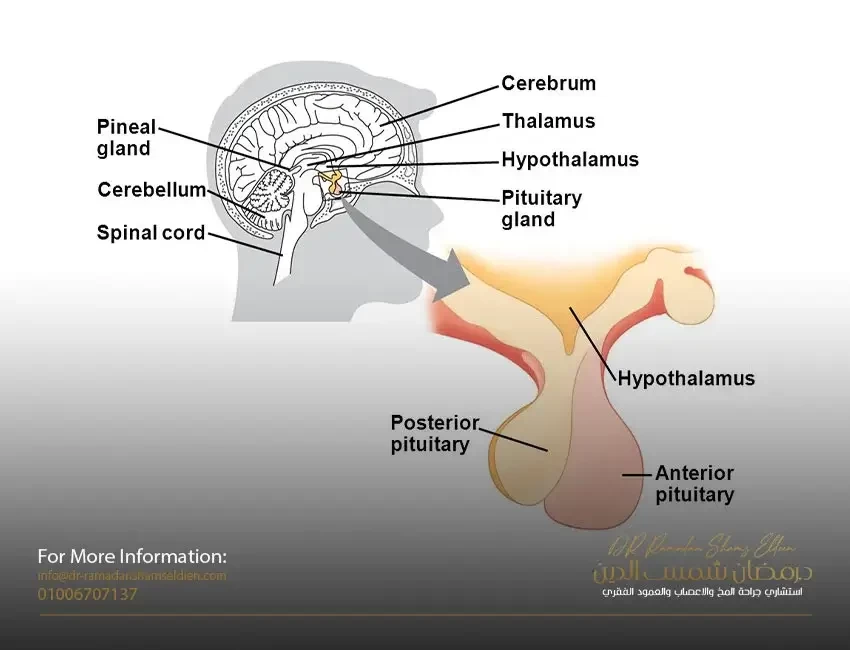
The hypothalamus is like a doctor who diagnoses, or identifies, a patient's illness or disease. It diagnoses the various sensory information that is transmitted to the brain including auditory (related to hearing or sound), visual, tactile, and taste cues. Next, it directs sensory information to different parts and lobes of the cortex. If this part of the brain is damaged, all the sensory information will not be processed and sensory confusion will result.
The hypothalamus is mainly responsible for motivational behavior.
This is why we know we are hungry or thirsty.
The hypothalamus also helps the body maintain a constant temperature.
This part of the brain also controls the pituitary gland, which is the main gland that controls all other endocrine glands in the body. Thus, the hypothalamus plays a major role in connecting the endocrine system with the nervous system.
The amygdala When you think of the amygdala, you should think of one word: fear. The amygdala is the reason we fear things that are out of our control. It also controls the way we react to certain stimuli, or events, that we see as threatening, the first of which is potential danger.
The hippocampus has a unique shape, similar to the shape of a horseshoe and a unique name. It is also the fortress of deep and lasting memory. The permanent storage place for all the information, experiences and events of a person throughout his life. We wouldn't even be able to remember where our home was without the hippocampus working. It has been proven that Alzheimer's disease (a disease that affects the elderly and often leads to memory loss) appeared as a result of a defect in this region of the brain.
The corpus callosum or the corpus callosum is the part of the brain that allows communication between the two hemispheres of the brain. It is responsible for transmitting nerve messages between the right and left hemispheres of the brain.
If we divide the brain into two equal halves, we will have a right and a left hemisphere. Although they are equal in size, these two aspects do not have the same functions.
The left side of the brain is responsible for controlling the right side of the body. It also performs tasks related to logic, such as in science and mathematics. On the other hand, the right hemisphere coordinates the left side of the body, and performs tasks related to creativity and the arts. Both cerebral hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum and serve the body in different ways.
The bridge or arch serves as a message station between several areas of the brain. It helps relay messages from the cortex and cerebellum. Without it, the brain would not be able to function because messages would not be able to be transmitted. It also plays a major role in sleep and dreaming, or the state of sleep where the dream is most likely to occur, and has been shown to originate in the pons region.
The medulla oblongata is easily the most important part of the brain. Where it controls and performs all involuntary functions without thinking. In fact, we would not be able to live without the marrow because of the myriad of critical functions it performs including regulating blood pressure and breathing. As part of the brainstem, it helps transmit nerve messages from the brain to the spinal cord.
How do we keep all these various brain functions dynamically and active all the time:
First, stay away from smoking
Smoking damages the nervous system in a large number of ways, both in the short and long term.
Mental stress, thinking and pressures of daily life in excess of the usual.
Sleep deprivation or sleep disturbance causes the parts of the brain that handle high-level functions to function less well
Malnutrition.